Exploring the role and importance of emotional intelligence in the educational landscape and its impact on students, educators, and overall academic success.
Introduction
Emotional intelligence (EQ) refers to the ability to recognize, understand, manage, and use emotions effectively in ourselves and others. In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the importance of emotional intelligence in the field of education. Research suggests that EQ plays a significant role in students’ academic achievement, mental health, and social development, as well as in the effectiveness of educators. This article will provide an in-depth look at emotional intelligence in education, discussing its key components, benefits, and strategies for promoting EQ in schools.
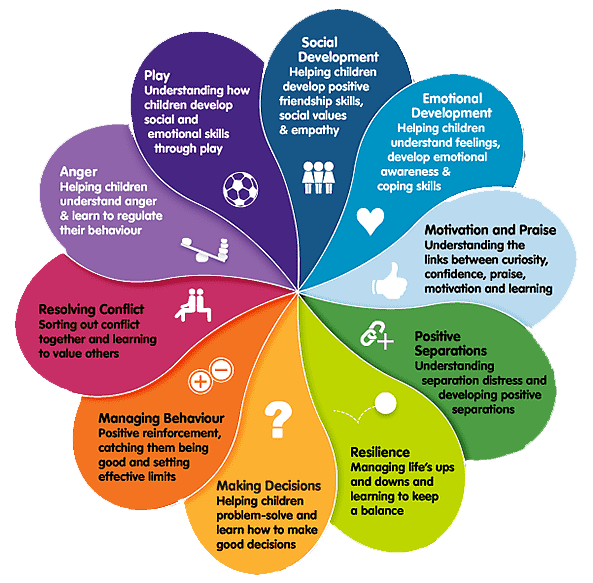
The Components of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is commonly defined as comprising five main components:
- Self-awareness: The ability to recognize and understand one’s own emotions, strengths, and weaknesses.
- Self-regulation: The ability to manage and control one’s emotions, impulses, and reactions in a healthy and appropriate manner.
- Motivation: The drive to set and pursue goals, overcome challenges, and achieve personal and professional success.
- Empathy: The ability to understand and share the emotions, feelings, and perspectives of others.
- Social skills: The ability to communicate, collaborate, and build positive relationships with others.
The Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Education
Emotional intelligence plays a crucial role in various aspects of education, including:
- Academic achievement: Research has shown a strong correlation between emotional intelligence and academic success. Students with high EQ tend to have better problem-solving skills, greater resilience, and more effective study habits, which contribute to improved academic performance.
- Mental health and well-being: Emotional intelligence is associated with better mental health and overall well-being. Students with high EQ are more likely to have effective coping strategies, lower levels of stress and anxiety, and a greater sense of self-worth and happiness.
- Social development: Developing emotional intelligence fosters better social skills and relationship-building abilities, helping students navigate social situations, form strong friendships, and work collaboratively with others.
- Classroom environment: A focus on emotional intelligence in education can create a more positive, supportive, and inclusive classroom environment, promoting a sense of belonging and reducing instances of bullying or negative behaviors.
The Role of Educators in Promoting Emotional Intelligence
Educators play a vital role in fostering emotional intelligence in their students. Some ways in which teachers can promote EQ in the classroom include:
- Creating a supportive and emotionally safe learning environment.
- Teaching students about emotions and providing them with the vocabulary to express their feelings.
- Encouraging open communication and active listening.
- Modeling emotionally intelligent behaviors, such as empathy, self-regulation, and effective communication.
- Integrating emotional intelligence lessons and activities into the curriculum.
- Providing opportunities for students to practice and develop their EQ skills through group work, role-plays, and other interactive activities.
Emotional Intelligence and Teacher Effectiveness
Emotional intelligence is not only important for students but also for educators. Teachers with high levels of EQ tend to be more effective and successful in their roles, as they can:
- Build stronger relationships with their students, creating a positive and supportive learning environment.
- Manage their own emotions and stress, resulting in better overall well-being and job satisfaction.
- Adapt their teaching strategies to meet the diverse emotional and learning needs of their students.
- Communicate effectively with parents, colleagues, and administrators, fostering collaboration and support.
Strategies for Developing Emotional Intelligence in Schools
Schools can take several steps to promote emotional intelligence among students and educators, such as:
- Providing professional development opportunities for teachers to learn about emotional intelligence and its importance in education.
- Integrating social-emotional learning (SEL) curriculum and programs that emphasize the development of emotional intelligence skills in students.
- Encouraging a school-wide culture that values emotional intelligence, including support from administrators, teachers, staff, and parents.
- Implementing mindfulness and stress-reduction practices to help both students and educators manage their emotions and improve overall well-being.
- Establishing partnerships with mental health professionals, such as school counselors or psychologists, to support students’ emotional development and address any concerns or challenges.
- Offering extracurricular activities and clubs that promote emotional intelligence, such as peer mentoring, conflict resolution, or community service initiatives.
Assessing and Monitoring Emotional Intelligence in Education
To ensure the effectiveness of emotional intelligence programs and initiatives, schools can implement various assessment and monitoring strategies, including:
- Utilizing emotional intelligence assessments or inventories to measure students’ EQ levels and track their progress over time.
- Observing and evaluating the emotional climate of classrooms and the school as a whole, identifying areas of strength and opportunities for improvement.
- Gathering feedback from students, educators, and parents about the impact of emotional intelligence initiatives on academic performance, mental health, and social development.
- Conducting regular reviews and updates of emotional intelligence curricula and programs, ensuring they remain relevant and effective in meeting the needs of students and educators.
The Future of Emotional Intelligence in Education
As our understanding of the importance of emotional intelligence in education continues to grow, it is likely that schools will increasingly prioritize the development of EQ in students and educators. This may include:
- Greater emphasis on social-emotional learning and emotional intelligence in teacher preparation programs, ensuring that new educators enter the profession with a strong foundation in EQ.
- Increased investment in resources, materials, and professional development opportunities related to emotional intelligence in education.
- The development of new and innovative strategies for promoting emotional intelligence, leveraging technology and research to enhance the effectiveness of EQ programs and initiatives.
- A greater focus on collaboration between schools, families, and communities in supporting the emotional development of students, recognizing the interconnectedness of these various influences on students’ lives.
Conclusion
Emotional intelligence plays a critical role in the success and well-being of students and educators alike. By understanding the importance of EQ in education and implementing strategies to promote its development, schools can create a more positive, supportive, and effective learning environment for all. As we continue to learn more about the impact of emotional intelligence on academic achievement, mental health, and social development, it is essential that schools prioritize and invest in the cultivation of these vital skills.


