Introduction
Emotional intelligence (EI) has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential to contribute to personal and professional success. While traditionally, academic success has been linked primarily to cognitive intelligence (IQ), research has increasingly highlighted the role emotional intelligence plays in students’ academic performance. This article will explore the connection between emotional intelligence and academic success and discuss the importance of integrating EI into the educational system.
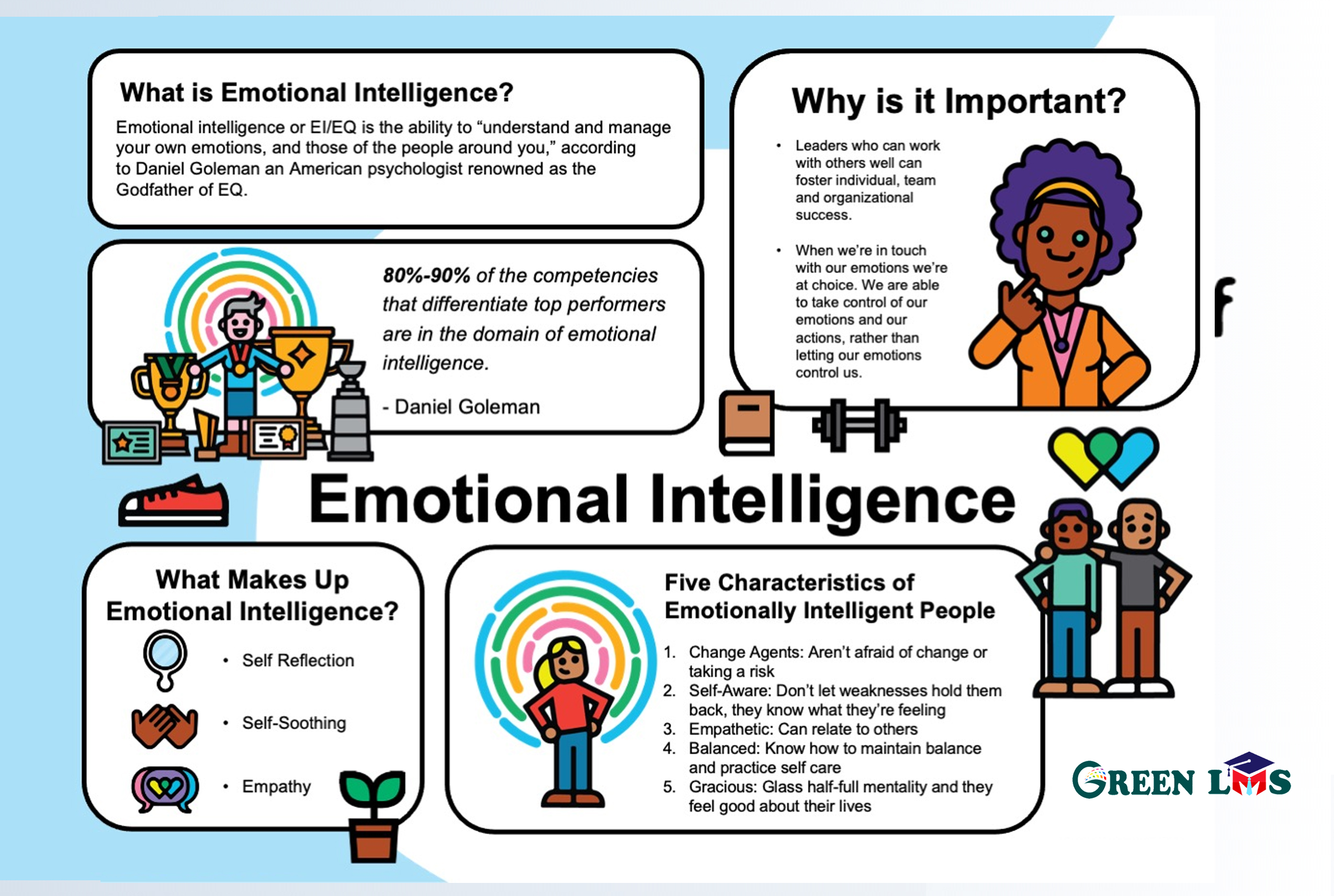
Understanding Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s own emotions and the emotions of others. It consists of five key components:
- Self-awareness: The ability to identify and understand one’s own emotions and their impact on thoughts and actions.
- Self-regulation: The ability to manage emotions effectively and appropriately.
- Motivation: The drive to achieve goals and persevere despite challenges.
- Empathy: The capacity to understand and share the feelings of others.
- Social skills: The ability to build and maintain healthy relationships, communicate effectively, and collaborate with others.
The Relationship Between Emotional Intelligence and Academic Success
Research has demonstrated a strong correlation between emotional intelligence and academic performance. Students with high EI tend to perform better academically for several reasons:
- Enhanced concentration: Emotionally intelligent students can better manage stress and distractions, allowing them to maintain focus and concentration during lessons and exams.
- Effective problem-solving: EI enables students to approach challenges with creativity, critical thinking, and adaptability, leading to better performance on assignments and tests.
- Positive attitude towards learning: Emotionally intelligent students are more likely to be motivated, engaged, and persistent in their studies, which contributes to higher academic achievement.
- Strong interpersonal skills: Students with high EI can build and maintain positive relationships with their peers and teachers, creating a supportive learning environment that fosters academic success.
Integrating Emotional Intelligence into Education
Recognizing the link between emotional intelligence and academic success, educators and policymakers must prioritize the integration of EI into the educational system. Here are some strategies for promoting EI in schools:
- Incorporate social-emotional learning (SEL) into the curriculum: Implement SEL programs that teach emotional intelligence skills alongside traditional academic subjects, helping students develop self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and effective communication.
- Train teachers in emotional intelligence: Provide professional development opportunities for teachers to enhance their understanding of EI and learn strategies for teaching these skills in the classroom.
- Create a supportive learning environment: Encourage a school culture that values emotional intelligence, fosters open communication, and promotes empathy and understanding among students and staff.
- Assess and monitor students’ emotional intelligence development: Use assessment tools to measure students’ growth in social-emotional competencies and inform instruction and intervention strategies.
The Long-term Benefits of Emotional Intelligence in Education
Promoting emotional intelligence in education not only leads to improved academic performance but also has long-term benefits for students’ personal and professional lives. Students who develop strong EI skills are more likely to:
- Build healthy relationships: Emotionally intelligent individuals can navigate interpersonal challenges and maintain strong connections with friends, family, and colleagues.
- Adapt to change and adversity: EI fosters resilience and adaptability, enabling individuals to cope with setbacks and navigate life’s challenges with grace and perseverance.
- Excel in their careers: Emotional intelligence is highly valued in the workplace, as it contributes to effective communication, collaboration, and leadership skills.
- Experience overall well-being: Individuals with high EI tend to have better mental health, as they can recognize and manage their emotions effectively and maintain a positive outlook on life.
Emotional Intelligence and Study Habits
Developing emotional intelligence can also have a significant impact on students’ study habits, contributing to academic success. When students possess strong EI skills, they are more likely to:
- Set realistic goals: Emotionally intelligent students can set achievable and challenging goals, helping them stay focused and motivated in their studies.
- Manage time effectively: EI enables students to prioritize tasks and manage their time efficiently, reducing procrastination and ensuring timely completion of assignments.
- Seek help when needed: Students with high EI can recognize when they need assistance and are more likely to ask for help from teachers, peers, or tutors, enhancing their understanding of the material.
- Reflect on their learning: Emotionally intelligent students can engage in self-reflection, evaluating their progress and identifying areas for improvement, which promotes continuous growth and development.
Emotional Intelligence and Test-Taking Strategies
Emotional intelligence can also influence students’ performance on exams by enhancing their test-taking strategies. Emotionally intelligent students can:
- Manage test anxiety: Students with strong EI skills can recognize and manage their anxiety, allowing them to remain calm and focused during exams.
- Develop effective test-taking strategies: EI enables students to plan and implement effective approaches to exams, such as time management, identifying key information, and eliminating incorrect choices.
- Learn from mistakes: Emotionally intelligent students can view mistakes as learning opportunities, using feedback from exams to improve their understanding and performance in future assessments.
Emotional Intelligence and Lifelong Learning
By fostering emotional intelligence in schools, educators can promote a lifelong love of learning among their students. Emotionally intelligent students are more likely to:
- Be intrinsically motivated: EI helps students develop an internal drive to learn and grow, making them more likely to pursue new knowledge and skills throughout their lives.
- Embrace challenges: Emotionally intelligent students view challenges as opportunities for growth, rather than threats to their self-esteem, promoting a growth mindset and a love for learning.
- Remain adaptable and open-minded: EI enables students to adapt to new situations and information, promoting curiosity and a willingness to explore new ideas and perspectives.
Emotional Intelligence and Parental Support
Parents can play a significant role in fostering their children’s emotional intelligence and academic success. By supporting the development of EI at home, parents can:
- Model emotionally intelligent behavior: Parents who demonstrate self-awareness, empathy, and effective communication can provide a positive example for their children to emulate.
- Encourage emotional expression: Parents can create a safe space for their children to express their emotions and provide guidance on managing emotions effectively.
- Reinforce social-emotional learning: By reinforcing the social-emotional skills taught in school, parents can help their children apply these skills in various aspects of their lives, contributing to academic success and overall well-being.
Emotional Intelligence and Special Education
Emotional intelligence can be especially beneficial for students with special needs, as it can help them overcome challenges and thrive academically. By integrating EI into special education programs, educators can:
- Foster self-advocacy: Emotionally intelligent students with special needs can better understand their emotions and needs, empowering them to advocate for appropriate accommodations and support.
- Enhance social inclusion: Developing emotional intelligence can help students with special needs build meaningful relationships with their peers, promoting a sense of belonging and reducing social isolation.
- Improve emotional regulation: Students with special needs may experience heightened emotional sensitivity or difficulty regulating emotions. EI can help them develop strategies for managing their emotions effectively and navigating challenging situations.
Emotional Intelligence and Cultural Competence
Cultivating emotional intelligence in schools can also contribute to the development of cultural competence among students. Emotionally intelligent students are more likely to:
- Be open to diverse perspectives: EI enables students to approach new ideas and cultures with curiosity and respect, fostering an appreciation for diversity.
- Develop empathy for others: Emotionally intelligent students can empathize with individuals from different backgrounds, promoting understanding and reducing prejudice and discrimination.
- Communicate effectively across cultures: EI equips students with the skills necessary to navigate cross-cultural interactions with sensitivity and adaptability, contributing to positive intercultural relations.
Emotional Intelligence and Creativity
There is a growing body of evidence suggesting a connection between emotional intelligence and creativity. By fostering EI in schools, educators can promote creative thinking and problem-solving among students. Emotionally intelligent students are more likely to:
- Be open to new experiences: Emotionally intelligent students can approach novel situations with curiosity and flexibility, fostering a mindset conducive to creativity and innovation.
- Collaborate effectively: Students with high EI can work well with others, leveraging the diverse skills and perspectives of their peers to generate innovative solutions.
- Manage the emotional aspects of creativity: The creative process can be fraught with uncertainty and vulnerability. Emotionally intelligent students can navigate these emotions effectively, allowing them to take risks and embrace the creative process.
Emotional Intelligence and Career Readiness
Fostering emotional intelligence in schools can have a significant impact on students’ career readiness, preparing them for success in the workforce. Emotionally intelligent students are more likely to:
- Develop strong workplace relationships: EI enables students to build positive relationships with colleagues and supervisors, fostering a supportive work environment and enhancing job satisfaction.
- Excel in leadership roles: Emotionally intelligent individuals tend to be effective leaders, as they can empathize with their team members, communicate clearly, and make informed decisions.
- Adapt to changes in the job market: EI promotes adaptability and resilience, enabling students to navigate the challenges of an ever-evolving job market with confidence and agility.
Conclusion
Emotional intelligence is an essential factor in academic success and has far-reaching implications for students’ personal, social, and professional lives. By prioritizing the development of emotional intelligence in schools, educators can equip students with the skills necessary to succeed academically and thrive in their future endeavors.
Join the revolution towards inclusive, and accessible, including LMS for Universities, LMS for Schools, LMS for Corporate organizations. and effective LMS for education for all.